Quantitative data — think user preferences and demographics — and qualitative data, including behavior patterns and use cases, will strongly impact business decisions. Combining these two type of studies is paramount when you are looking to create a service that impacts certain communities or interests enough people.
But how do you get this vital, game-changing information? One way to gather qualitative and quantitative information is through surveys. Surveys help to reach a wide group of people and get a vast number of answers that you can then turn into hard data.
While the benefits of gathering qualitative and quantitative data is probably quite clear, you’re probably wondering how to design an effective survey and — more importantly — how to inspire enough people to take the survey.
Qualitative and quantitative data are different and each can even be used to measure data. But how do you even gather enough data to begin with? Well, you’ll need to maximize your response rates.
How To Maximize Response Rates
Surveys are a great way to get and record information, but they only work efficiently if people participate in them. Before you learn how to analyze data, you have to have enough of it. Below, we will outline a few ways to encourage people to participate in your survey.
Related: 20 Interactive Presentation Games
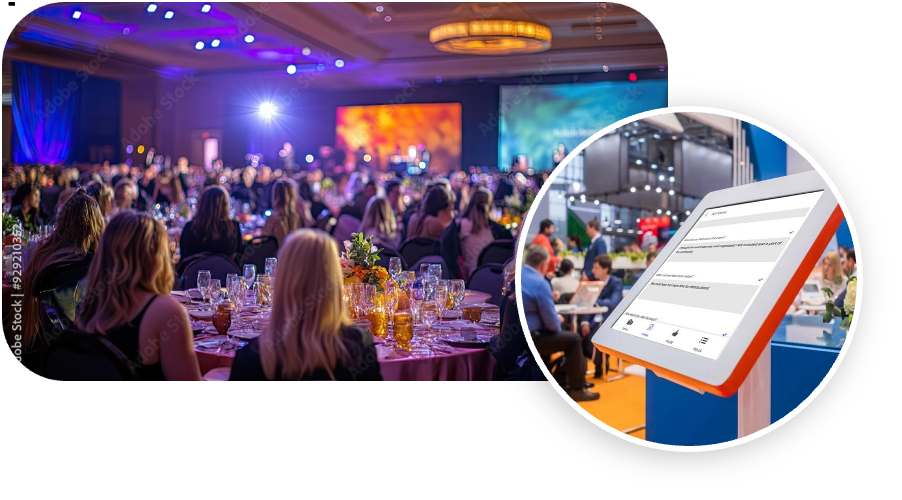
Take Surveys at Online Events
For the foreseeable future, live events may not be an option due to social distancing guidelines we must follow in the wake of the coronavirus pandemic. But that doesn’t mean there won’t be events you can utilize to get a massive amount of surveys filled out. A lot of companies are already utilizing online platforms to create virtual events, most oftenly hosting webinars on Zoom.
Online events range from tutorials and classes to interviews, tours, and performances. It’s a way for people to not just be entertained, but connect with other people while possibly sitting alone in their house for over a month. these online events have a captive audience who most likely paid to be granted access.
So just like live events, online events offer a time frame for people to fill out the survey without distractions like Netflix or cleaning the kitchen for the tenth time that week.
Using the chosen webinar platform’s chat service, you can ensure that everyone present receives a link to the survey. While it shouldn’t be a requirement, having an event that relates to the survey’s questions will further prompt people to take part.
Incentivize With a Raffle
Another way to boost survey engagement is to try and offer those who participate in a prize. If you’re looking to survey a few hundred people buying a prize for each individual may be costly and not feasible.
To help with this situation, you should offer a raffle with a grand prize. Everyone that participates in your survey will be entered into the raffle. Hopefully, this will boost engagement because those who participate will feel like they are getting free goodies for just answering a few questions.
Want to take a live survey and give out prizes? Try out the MeetingPulse Raffle feature.
Provide Digital, Not Physical Surveys
Digital surveys can be more effective than physical surveys because, first of all, most people are typically glued to a device. Whether they’re on their phone or laptop, clicking on a virtual link will be easier than getting up to collect a piece of paper, filling it out, and then figuring out where to put it afterward.
Digital surveys are also better for analysis purposes. You won’t have to manually input any data. It’s already there for you, and you can quickly convert it to visualizations or share it with your data analysis team to start drawing conclusions.
Related: How to Get People to Take a Survey
Designing Qualitative Survey Questions
These questions should be concise and identify exactly what you’d like to know. Since qualitative data is conceptual and descriptive, you should be asking questions along these lines.
How To Write Effective Qualitative Questions
To write a qualitative question that’s effective, you must first begin with the topic you’re surveying people about and what you want to know. If you’re asking people about a newly proposed building, you may ask them how they feel about the possibility of the new structure and why. Your questions should answer what you want to know while providing an explanation to help support your data.
To prompt people correctly, you must first format the questions in an engaging way that inspires people to answer. Try beginning with words like “how” and “what.” Ask “what happened” to craft your description, or ask what people felt about what happened to understand your results. You can even ask “what happened over time” to further explore the process.
Words to avoid using in the questions include:
- Relate
- Impact
- Effect
- Cause
- Influence
- Compare
- Contrast
Here’s an example of this in action:
Good qualitative research question: What do you like most about this video conference platform?
Bad qualitative research question: Do you like Meeting Pulse’s live audience response feature?
Qualitative questions should never be able to be answered with a simple “yes” or “no.” Instead, you are looking for answers with insight, depth, and thought.
The Value Of Open-Ended Questions
If you’re looking to get very descriptive answers for your qualitative survey, then asking open-ended questions is the best way to go. These questions will force those being surveyed to think about their answer and answer with detail. This helps your information collected to be more specific and not just a yes or no answer.
What To Use Qualitative Data For
Qualitative data focuses on words more so than numbers. This makes the data great for recording ideas, opinions, and statements. This will help you see if a community stands on the same ground or even help to get the feel of how people view a certain situation with greater specificity.
Designing Quantitative Survey Questions
Unlike qualitative, quantitive survey questions will be number oriented. These are great for gauging how people feel or even asking how likely they are to do something by providing them with a scale. One of the key benefits of quantitative questions is how straightforward the data is. They’re easier to answer, standardize, and to compare.
The Value of Numerical Data
Numerical data is very valuable because it turns survey answers into hard facts. Pulling a percentage will help support an argument or even give you an idea for where people stand. Overall, numerical data is hard to argue with as long as it was collected correctly. Numerical data is also easier to use for graphs, charts, and other visualizations.
Types of Quantitative Formats
Multiple Choice
One of the best ways to give a survey is by making it multiple choice, especially if it’s quantitative. This will make it easier for people to answer. You can compare the number of choices for each of the four or five multiple-choice answers and convert this data into a pie chart or bar graph.
Rating

Another great way to survey people quantitatively is by using a scale. Using a scale of 1 to 10 will help gauge how people feel. For example:
How would you rate Meeting Pulse’s live polling options?
1: Not at all, I don’t understand it or don’t enjoy it
5: It’s pretty good, but can use some improvements
10: It’s excellent, kept me engaged and made me feel heard
What To Use Quantitative Data For
Gathering quantitative data is preferable when you’re simply looking for results, not the meaning behind the results. They can use this data type to address questions like “how many,” “how much,” or “what aspects.” Overall, it’s data that can be counted and scaled, which provides a great platform to back up statements with hard facts.
How To Strike a Balance
When surveying people you should be using qualitative and quantitative data to your advantage. To get the most detailed answers and most specific answers you should be asking a mixture of both. Using both types of data will make your collected data stronger and help to narrow down the information you gather.
What Is Your Purpose?
To have a successful survey that has a great balance of quantitative and qualitative questions, you must first ask yourself what the purpose of the survey will be. Will it be to gather hard numerical information that needs qualitative support? Or will it be to gather qualitative data that needs just a little of numerical support.
Focusing and narrowing down what you want out of the survey will help you to create it and put in the right balance of questions needed to get the answers you want. Both qualitative and quantitative answers will back one another, but to have a strong outcome both types are better than just one.
How To Analyze Data

People will generally say there are 5 steps to analyzing data.
- The first step is to define your questions. Make sure you’re asking a good mix of quantitative and qualitative questions that relate to the outcome you want to see.
- The second step is to determine measurement priorities. You need to know what you’ll be measuring (for example how people feel about something) and know how you’ll be measuring it (such as time frame).
- After this is figured out, the third step is to collect the data. After you have surveyed people it’s time to move onto step four — analyzing it.
- You can analyze your data by placing it in a spreadsheet or recording each answer as you come across it manually. The fifth and final step is interpreting the data collected.
- Determine if you need more. Did you get the data you wanted and how does it compare to what you thought? Is it enough to back up your argument or statement? If you need more data at this point you may have to do the process all over again.
Related: Using Polling Software to Boost Employee Feedback and Engagement
Examples of Using Qualitative and Quantitative Questions Together
If you’re having trouble coming up with a survey that includes both quantitative and qualitative data, here’s an example. Please see our example questions below:
What coffee drink do you order often? (quantitative)
- Latte
- Black coffee
- Americano
- Other:
What do you like most about your preferred drink choice above? (qualitative)On a scale of 1 to 10, how likely are you to recommend this drink to a close friend, with 10 being the most likely? (quantitative)Why did you choose the number above? (qualitative)
Getting Started Collecting Data
We have given you a rundown on qualitative and quantitative data. You know that qualitative further clarifies why the person being surveyed chose their answer and that quantitative will help to provide real numbers to be recorded. You can use a combination of the two to gain a more comprehensive view on any topic.
To collect both quantitative and qualitative data, you can use a live polling tool like MeetingPulse. You can integrate it into your Powerpoint presentations or just send out links, boosting engagement by providing surveys during online events and meetings.
With Meeting Pulse, you can ask multiple choice questions, yes or no questions, and short answer questions. You can even ask conditional questions if you want to collect insight from a subset of your audience.
Find out more about live audience surveys with MeetingPulse here.